Concepts
Note: The citations in this page have their correspondent reference in the Zotero library online which contains our recommended readings.
Definitions in the domain of vocabularies are not unique or clearly established. It is important, to facilitate communication, make explicit what meaning are you attaching to a certain term. We offer here a summary of basic terminology with pointers to useful definitions and sources.
Application profile
"An Application Profile is a data specification to facilitate the data exchange in a well-defined application context. It re-uses concepts from one or more semantic data specifications, while adding more specificity, by identifying mandatory, recommended, and optional elements, addressing particular application needs, and providing recommendations for controlled vocabularies to be used" (Interoperable Europe Portal, 2023)
Authority list
Also called "Authority files" are lists (see: List) produced by an authoritative entity (e.g., a government or cultural heritage institution), which are meant to be reliable and "permanent". "authority data is a community convention and an information infrastructure" (Romein et al., 2023)
Controlled vocabulary
“A controlled vocabulary is an organized arrangement of words and phrases used to index content and/or to retrieve content through browsing or searching. It typically includes preferred and variant terms and has a defined scope or describes a specific domain.” (Harpring, P., 2010)
See also: Vocabulary, Taxonomy
Classification scheme
- "In information sciences, classification schemes are used to organise information: You have a list of unequivocal terms and a rule prescribing, at least in a certain application context, to refer to phenomena of your domain of interest exclusively using the terms from your list (i.e. you have a controlled vocabulary), and you apply terms of your vocabulary to multiple pieces of your data and thus facilitate data profiling, and information retrieval." (Romein et al., 2023).
- Hierarchical and faceted arrangements of numerical or alphabetical notations to represent broad topics. (Zeng, 2008)
- As Romein et al., 2023 indicate all other types of knowledge organization system could express or be used as classification schemes.
Gazetteer
"A gazetteer is a dictionary of place names. Traditional gazetteers have been published as books or they appear as indexes to atlases. Each entry may also be identified by feature type, such as river, city, or school. Geospatially referenced gazetteers provide coordinates for locating the place on the earth's surface. An example is the Geographic Names Information Service http://www-nmd.usgs.gov/www/gnis/. Note that the term "gazetteer" has several other meanings including an announcement publication such as a patent or legal gazetteer. These gazetteers are often organized using classification schemes or subject categories." (NKOS, 2000) "Gazetteers can be regarded as a special kind of authority file." (Zeng, 2008).
See also: Authority File
Knowledge graph
- "The diversity of knowledge graph use extends from mostly attribute characterizations of instances (such as the Google Knowledge Graph) to mostly conceptual frameworks akin to upper-level ontologies. Attempts to provide a “precise” definition of KGs appear likely doomed to failure [...] Given the diversity of use, I also agree with the advice of Hogan et al. [11] who “strongly encourage researchers who wish to refer to ‘Knowledge Graphs’ as their object of study to rigorously define how they instantiate the term as appropriate to their investigation.” While we may not find a precise definition across all uses of knowledge graphs, we should strive to define how they are used in specific contexts." (Bergman, 2019)
- "We tend to define knowledge graphs as complete knowledge bases of concepts and instances and their attributes, coherently organized into types and a logical and computable graph, and written in RDF, SKOS, and OWL 2." (Bergman, 2019)
See also: Ontology
Knowledge Organization Systems (KOS)
-
"The designation knowledge organization system, while not used as widely in the business world as it is in academia, is becoming more recognized, especially with increasing adoption of the World Wide Web Consortium’s (W3C) recommended framework for representing these various controlled vocabularies, called Simple Knowledge Organization System (SKOS)." (Hedden, 2022)
-
The designation knowledge organization system was first used by the Networked Knowledge Organization Systems Working Group at its initial meeting at the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) Digital Libraries Conference in Pittsburgh, Pa., in 1998." (Hedden, 2022)
-
“Knowledge organization system” (KOS) “has been adopted as a general term to encompass all schemes used to organise information and promote knowledge management, such as classification schemes, gazetteers, lexical databases, taxonomies, thesauri, and ontologies. These KOSs aim to underline the semantic structure of a domain” (Corcho et al., 2024)
-
Typology of KOS by (Zeng, 2008)
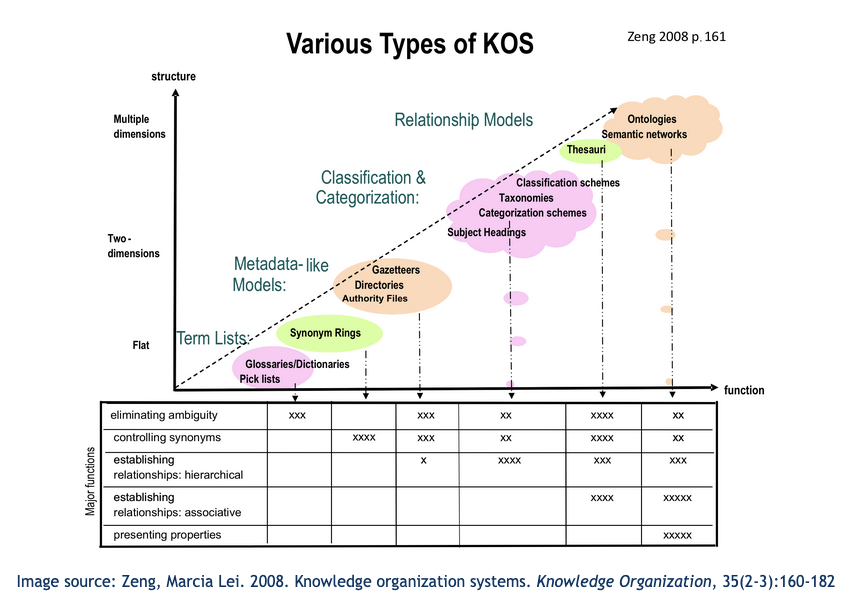
-
Typology of KOS by (Blumauer, 2015)
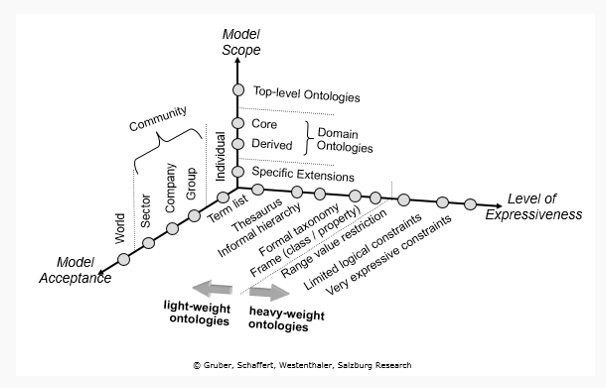
-
Typology of KOS by (Hedden, 2022):
- Term lists (authority files, glossaries, dictionaries, and gazetteers)
- Classifications and categories (subject headings, classification schemes, taxonomies, and categorization schemes)
- Relationship lists (thesauri, semantic networks, and ontologies)
See also: Vocabulary; Semantic artefact
List
Lists "provide information about individuals (‘particulars’) of a certain kind" (Romein et al., 2023)
Ontology
Especially this concept is subject to different definitions depending on the domain. There is not a single, agreed-upon definition of ontology. It is important to make explicit what are you referring to when you use this term. These are some of the most common definitions:
- "An ontology consists of a schema along with a taxonomy." (Kagle, 2025)
- "Some form of conceptual schema governs every knowledge structure used for knowledge representation (KR). In the semantic Web, such schemata are known as ontologies, since they attempt to capture the nature or being (Greek ὄντως, or ontós) of the knowledge domain at hand. Because the word ‘ontology’ is a bit intimidating, a better variant is the knowledge graph (because all semantic ontologies take the structural form of a graph). In general knowledge domains, we call such schemata upper ontologies." ()
- "An ontology is a ‘formal, explicit specification of a shared conceptionalization’ (Guarino et al. 2009) of a domain of the world. It describes what type of entities can exist in this domain and what relationships they may have. (On the distinction between ontologies and thesauri, cf. Kless et al. 2015.)" (Romein et al., 2023)
See also: Knowledge graph, Controlled vocabularies
Semantic artifact
"Semantic artefacts (SA) –a broad term to include ontologies, terminologies, taxonomies, thesauri, vocabularies, metadata schemas and semantic standards– are key for the description of data and for making data FAIR." (Wilson & Jonquet, 2024) “In the context of this article, we define a semantic artefact as a machine-actionable formalisation (represented using appropriate formats and serialisations, including RDF and non-RDF standards) of a conceptualisation, enabling sharing and reuse by humans and machines.”
Schema
- Often used as synomym of "Data model" and "Ontology" (Hyvönen & Tuominen, 2024)
Scheme:
- Sometimes used to refer to the "values" of controlled vocabularies.
See also: Classification scheme
Subject heading
"This scheme provides a set of controlled terms to represent the subjects of items in a collection. Subject heading lists can be extensive, covering a broad range of subjects. However, the subject heading list's structure is generally very shallow, with a limited hierarchical structure. In use, subject headings tend to be pre-coordinated, with rules for how subject headings can be joined to provide more specific concepts. Examples include the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) and the Library of Congress Subject Headings (LCSH)." (NKOS, 2000)
See also: Scheme
Taxonomy
-
"In the context of knowledge systems, taxonomy is the hierarchical classification of entities of interest of an enterprise, organization or administration, used to classify documents, digital assets and other information. Taxonomies can cover virtually any type of physical or conceptual entities (products, processes, knowledge fields, human groups, etc.) at any level of granularity." (Bergman, 2019)
-
"The presence of hierarchical relationships among concepts is what makes a simple controlled vocabulary into what is best known as a taxonomy." (Hedden, 2022).
-
According to both ANSI/NISO Z39.19-2005 and ISO 25964-1: 2011 thesaurus standards, there are three kinds of hierarchical relationships (Hedden, 2022):
- Generic or generic–specific: "a kind of", e.g., Laptops are a kind of computer
- Instance: named individuals, e.g., New Year’s Day is a specific instance of holidays.
- !Warning: "The relationship between a concept and the name of its facet or concept scheme is not a true hierarchical relationship." E.g., A Concept Scheme or Facet (e.g., "Animal Types Vocabulary" or "Genre Facet") is not a concept, it's a container or grouping.
- Whole–part: “is within” or “is a constituent part of”, e.g., Marine biology is a part of biology.
-
"For present-day information management, the term taxonomy is used both in the narrow sense to mean a hierarchical structure of terms or concepts, and in the broad sense in reference to any set of controlled vocabularies used to tag or classify content to support information retrieval [...] However, as previously explained, this book uses a broader definition of taxonomy that encompasses all kinds of controlled vocabularies. So, we will refer to taxonomies that are structured as hierarchies as hierarchical taxonomies." (Hedden, 2022).
Thesaurus
- "A controlled and structured vocabulary in which concepts are represented by terms, organized so that relationships between concepts are made explicit, and preferred terms are accompanied by lead-in entries for synonyms or quasi-synonyms." (ISO 25964-1:2011)
Vocabularies
See also: Controlled vocabularies; Knowledge organization system